AggreWell™ 微孔板
简便、可重复的 3D 球状体和拟胚体生产
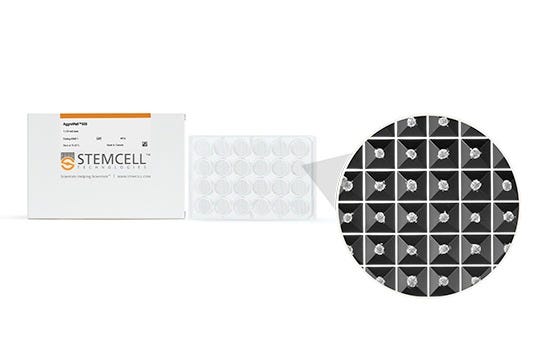
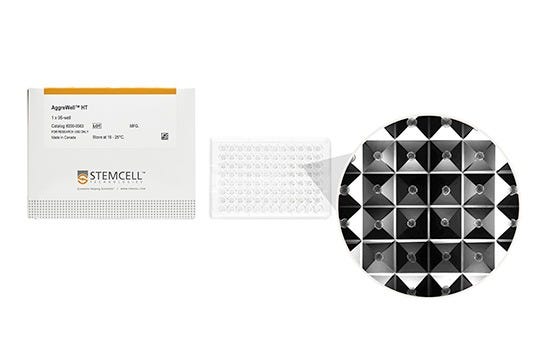
AggreWell™ 微孔板包含尺寸为 400 µm (AggreWell™400)、800 µm (AggreWell™800)或900 µm (AggreWell™HT)的微孔,可灵活生成您研究中所需大小的细胞球。
AggreWell™ 工作原理是什么?
观看此简短视频,详细了解 AggreWell™ 如何生成尺寸和形状均一的 3D 球状体和拟胚体。
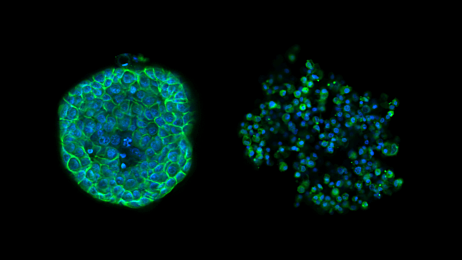
要使用 AggreWell 制备球状体或拟胚体,只需将单细胞悬液加入微孔板中,然后通过离心使细胞均匀分布到各个微孔内。孵育过夜,在 24–48 小时后评估球状体的形成情况。之后可以继续在微孔中培养,或收集类球状体进行后续分析实验。
为什么使用 AggreWell™ 来生成 EB 和球状体?
- 使用简单的操作流程即可生成球状体和拟胚体。
- 可大量生成尺寸和形状均一的类球状体,确保实验结果的稳定性。
- 通过调整细胞接种浓度,灵活控制类球状体的大小。
- 每孔可生成高达 5,900 个球状体。
- 使用一块微孔板即可大规模生成类球状体和类胚体,单个球状体成本不到一美分。
科学资源
Key Applications and Related Publications
ES and iPS Cell Directed Differentiation (Selected)
Cheung et al. (2014) Telomerase protects werner syndrome lineage-specific stem cells from premature aging. Stem Cell Reports 2(4):534-46
Hartjes et al. (2014) Selection via pluripotency-related transcriptional screen minimizes the influence of somatic origin on iPSC differentiation propensity. Stem Cells 32(9):2350-9
Jang et al. (2014) Culture of Pig Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells without Direct Feeder Contact in Serum Free Media. J Stem Cell Res Ther 4(2):174
Kinney et al. (2014) Mesenchymal morphogenesis of embryonic stem cells dynamically modulates the biophysical microtissue niche. Sci Rep 4: 4290
Kokkinaki M. (2011) Human Induced Pluripotent Stem-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Cells Exhibit Ion Transport, Membrane Potential, Polarized Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Secretion, and Gene Expression Pattern Similar to Native RPE. STEM CELLS 29:825–835
Nguyen et al. (2014) Microscale Generation of Cardiospheres Promotes Robust Enrichment of Cardiomyocytes Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cell Reports 3(2): 260–268
Sebastiano V et al. (2014) Human COL7A1-corrected induced pluripotent stem cells for the treatment of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Sci Transl Med 6(264):264ra163
Ungrin et al. (2012) Rational bioprocess design for human pluripotent stem cell expansion and endoderm differentiation based on cellular dynamics. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(4): 853-66
van Wilgenburg et al. (2013) Efficient, long term production of monocyte-derived macrophages from human pluripotent stem cells under partly-defined and fully-defined conditions. PloS one 8(8):e71098
Cancer Spheroid Research
Razian et al. (2013) Production of Large Numbers of Size-controlled Tumor Spheroids Using Microwell Plates. J Vis Exp. 81: 50665
Wrzesinski et al. (2014) The Cultural Divide: Exponential Growth in Classical 2D and Metabolic Equilibrium in 3D Environments. PLoS ONE 9(9): e106973
Drug Screening & Drug Delivery
Bratt-Leal A et al. (2013). A microparticle approach to morphogen delivery within pluripotent stem cell aggregates. Biomaterials 34(30): 7227-35
Fey et al. (2012) Determination of drug toxicity using 3D spheroids constructed from an immortal human hepatocyte cell line. Toxicol Sci 127(2): 403-11
Lim et al. (2011) Development of nano- and microscale chondroitin sulfate particles for controlled growth factor delivery. Acta Biomater 7(3): 986-95
Lei et al. (2014) Characterization of a multilayer heparin coating for biomolecule presentation to human mesenchymal stem cell spheroids. Biomater Sci 2: 666-673
Disease Modeling
Aflaki et al. (2014) Macrophage models of Gaucher disease for evaluating disease pathogenesis and candidate drugs. Sci Transl Med. 11;6(240): 240ra73
Moya et al. (2013) An integrated model of perfused tumor and cardiac tissue. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 4(Suppl 1):S15
3D Tissue Engineering
Cho et al. (2013) Generation of human secondary cardiospheres as a potent cell processing strategy for cell-based cardiac repair. Biomaterials 34(3): 651-61
Cimetta et al. (2014) Microscale technologies for regulating human stem cell differentiation. Exp Biol Med. 239(9):1255-63
Kabiri et al. (2012) 3D mesenchymal stem/stromal cell osteogenesis and autocrine signalling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 419(2): 142-7
Suspension Culture of MSCs
Baraniak et al. (2012) Scaffold-free culture of mesenchymal stem cell spheroids in suspension preserves multilineage potential. Cell Tissue Res. 347(3): 701-11
Cook et al. (2012) Micromarrows - Three-dimensional coculture of hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stromal cells. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods 18(5): 319-328
Rettinger et al. (2014) In vitro characterization of scaffold-free three-dimensional mesenchymal stem cell aggregates. Cell Tissue Res 358(2): 395-405
Additional Applications
Wallace et al. (2013) Using 3D culture to investigate the role of mechanical signaling in keratinocyte stem cells. Methods Mol Biol 989: 153-64
AggreWell™ Background
Ungrin et al. (2008) Reproducible, ultra high-throughput formation of multicellular organization from single cell suspension-derived human embryonic stem cell aggregates. PLoS One 3(2) e1565


 EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒
EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒









 沪公网安备31010102008431号
沪公网安备31010102008431号