技术资料
-
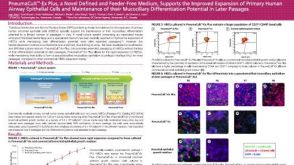 科学海报PneumaCult™-Ex Plus, a Novel Defined and Feeder-Free Medium, Supports the Improved Expansion of Primary Human Airway Epithelial Cells
科学海报PneumaCult™-Ex Plus, a Novel Defined and Feeder-Free Medium, Supports the Improved Expansion of Primary Human Airway Epithelial CellsConference:
American Thoracic Society Conference 2017
-
 科学海报Positive Selection of PE- or Biotin-Conjugated Antibody Labeled Cells with Releasable Rapidspheres™
科学海报Positive Selection of PE- or Biotin-Conjugated Antibody Labeled Cells with Releasable Rapidspheres™Conference:
AAI 2017
-
 挂图SnapShot: Breast Cancer Overview of signaling pathways, commonly mutated genes and breast cancer subtypes
挂图SnapShot: Breast Cancer Overview of signaling pathways, commonly mutated genes and breast cancer subtypes


 EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒
EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒










 沪公网安备31010102008431号
沪公网安备31010102008431号