技术资料
-
 点播Human T Cell Expansion Course Learn how to optimize your T cell culture and expansion protocol.
点播Human T Cell Expansion Course Learn how to optimize your T cell culture and expansion protocol. -
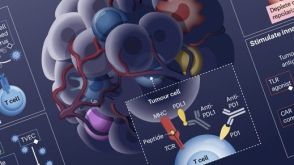 挂图Rational Combination of Cancer Therapies with PD1 Axis Blockade Lists the ways to combine new immunotherapeutic targets and modalities for your translational research.
挂图Rational Combination of Cancer Therapies with PD1 Axis Blockade Lists the ways to combine new immunotherapeutic targets and modalities for your translational research.


 EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒
EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒







 沪公网安备31010102008431号
沪公网安备31010102008431号