产品号 #100-0016_C
用于从人 ES 和 iPS 细胞衍生的星形胶质细胞前体生成皮质型星形胶质细胞的成熟试剂盒
若您需要咨询产品或有任何技术问题,请通过官方电话 400 885 9050 或邮箱 info.cn@stemcell.com 与我们联系。
用于从人 ES 和 iPS 细胞衍生的星形胶质细胞前体生成皮质型星形胶质细胞的成熟试剂盒
用于从人 ES 和 iPS 细胞衍生的星形胶质细胞前体生成皮质型星形胶质细胞的成熟试剂盒
STEMdiff™ 星形胶质细胞成熟试剂盒用于快速高效地将通过 STEMdiff™ 星形胶质细胞分化试剂盒(目录号 #100-0016)从人类多能干细胞(hPSCs)衍生的星形胶质前体分化为皮层型的星形胶质细胞。使用该系统,最快可在 7 周内从 hPSC 中分离出高纯度的星形胶质细胞群(平均 S100B 阳性细胞 > 70%、GFAP 阳性细胞 > 60%;双皮质素阳性细胞 < 15%),并可在培养中长期维持。使用这些产品分离的细胞可作为构建人类神经发育和疾病模型、药物筛选、毒性测试和细胞疗法验证的多功能工具。
分类
专用培养基
细胞类型
星形胶质细胞,神经细胞,PSC衍生
种属
人
应用
细胞培养,分化,功能学筛选
品牌
STEMdiff
研究领域
疾病建模,药物发现和毒理检测,神经科学
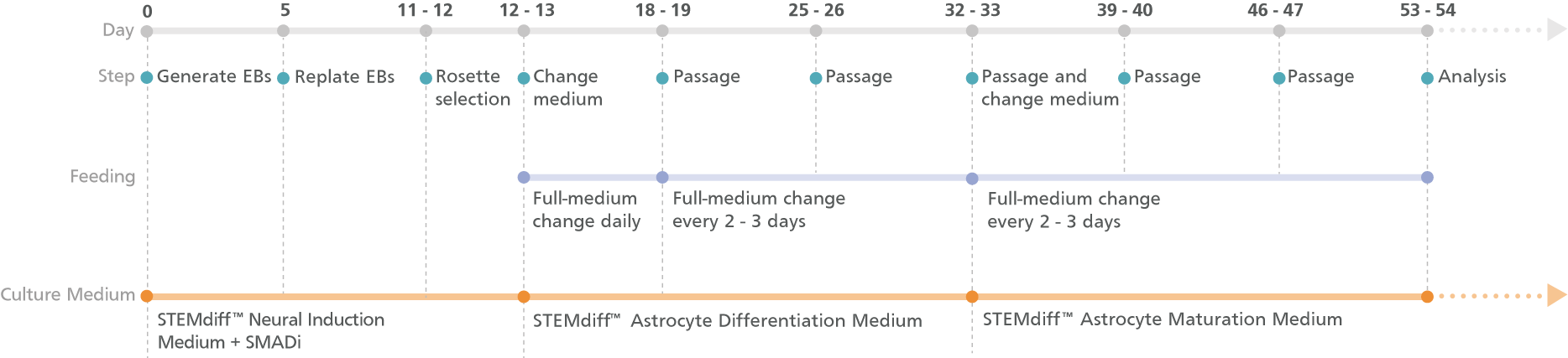
Figure 1. Schematic for the Embryoid Body Protocol
Cortical-type astrocytes can be generated from astrocyte precursors after 20 days in STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation Medium. For differentiation of precursors from embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells, see the PIS.
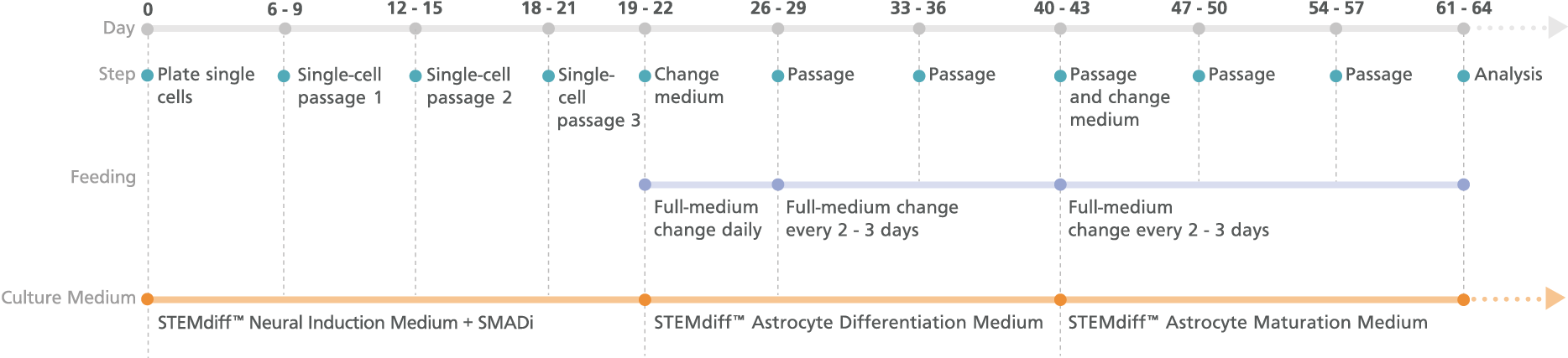
Figure 2. Schematic for the Monolayer Protocol
Cortical-type astrocytes can be generated from astrocyte precursors after 21 days in STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation Medium. For differentiation of precursors from embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells, see the PIS.
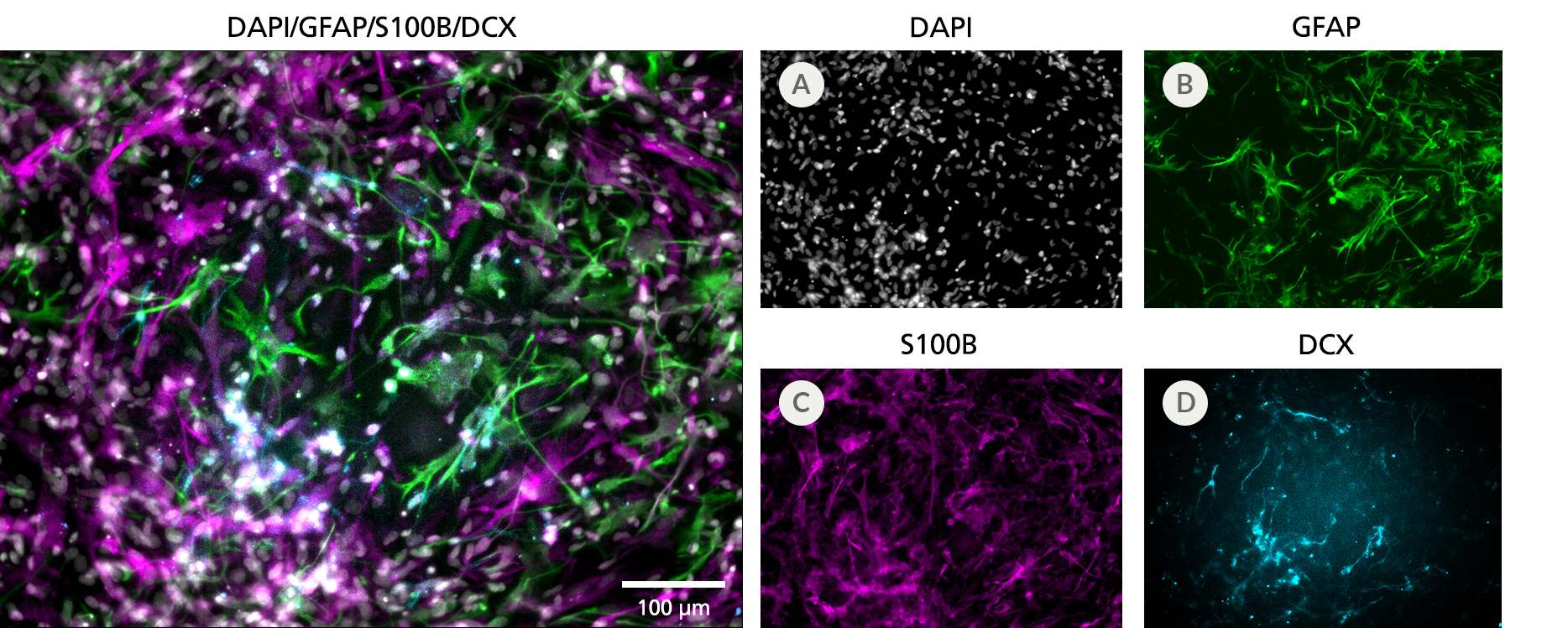
Figure 3. Cortical-Type Astrocytes Are Generated After Culture in STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation and Maturation Kits
NPCs generated from hPSCs in TeSR™-E8™ using the STEMdiff™ SMADi Neural Induction Kit embryoid body (EB) protocol were differentiated and matured to cortical-type astrocytes using the STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation and Maturation Kits. Cortical-type astrocytes were formed after iPS cell-derived NPCs were cultured with the STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation Kit for 3 weeks and STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Maturation Kit for 3 weeks. (A) Nuclei are labeled with DAPI (gray). The resulting cultures contain a highly pure population of astrocytes, which are (B) more than 60% GFAP-positive (green) and (C) more than 70% S100B-positive (magenta), with (D) fewer than 15% neurons (DCX-positive cells, cyan). Scale bar = 100 μm.
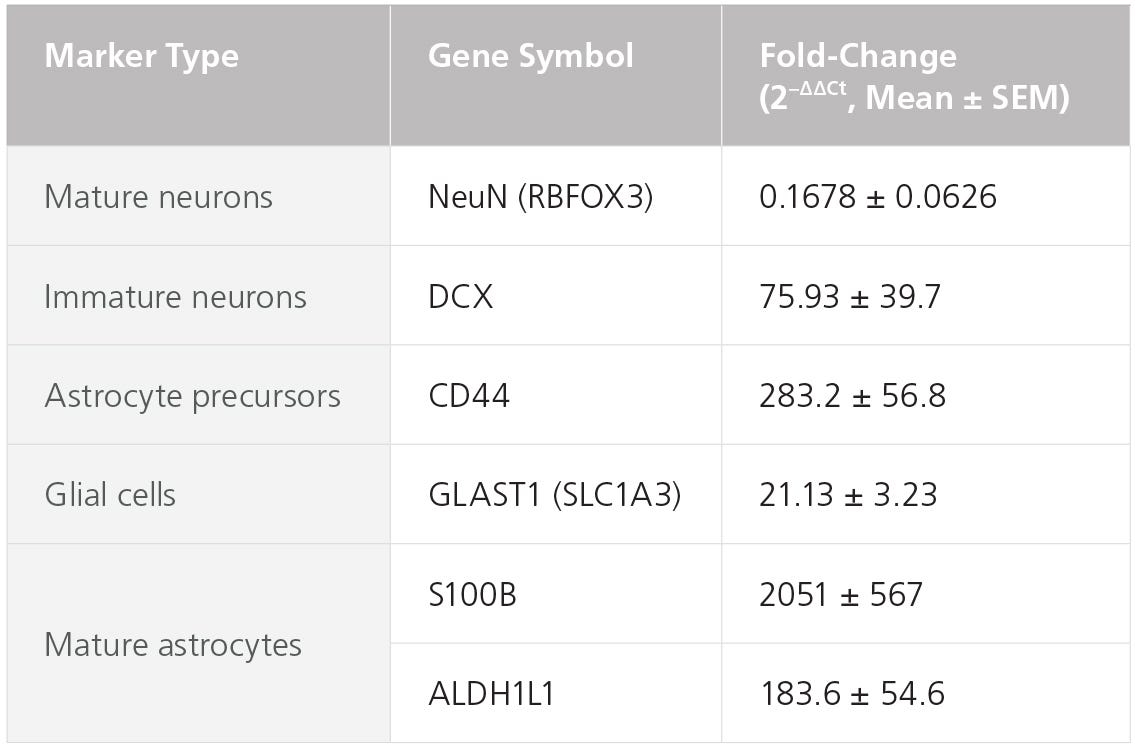
Figure 4. STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Kits Generate Cells Expressing Expected Levels of Genes Characteristic for Astrocytes
Embryonic stem and induced pluripotent stem cells from a variety of lines (n = 6, maintained in mTeSR™1 or TeSR™-E8™) were differentiated to NPCs using the STEMdiff™ SMADi Neural Induction Kit embryoid body protocol. Cells were then grown in STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation Kit for 3 weeks followed by STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Maturation Kit for 3 weeks prior to analysis. Expression levels were measured by quantitative PCR (qPCR) and normalized to hPSC controls relative to housekeeping genes 18S and TBP.
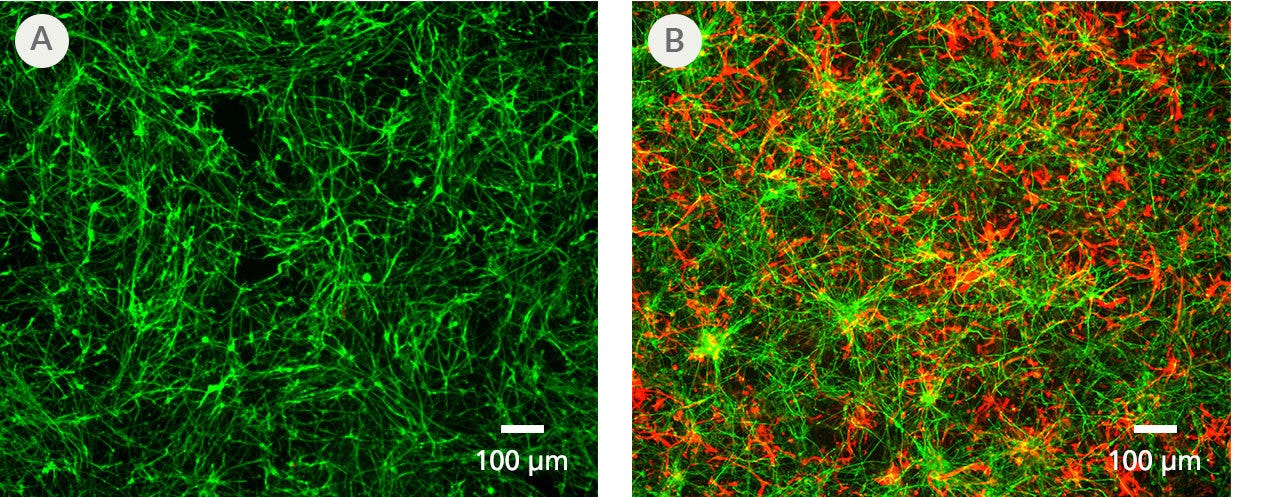
Figure 5. PSC-Derived Astrocytes and Neurons Can Be Co-Cultured to Model Cell-Cell Interactions In Vitro
NPCs generated from the H1 cell line were differentiated to astrocytes using STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation and Maturation Kits. H9 cell-derived NPCs were differentiated to forebrain-type neurons using STEMdiff™ Forebrain Neuron Differentiation and Maturation Kits. For co-culture, matured astrocytes were seeded onto forebrain neurons that had been in STEMdiff™ Forebrain Neuron Maturation Medium for at least one week. Co-cultures were then switched to STEMdiff™ Forebrain Neuron Maturation Medium the following day and for the remaining co-culture. (A) Neurons cultured alone, following the co-culture feeding schedule, are labeled with DCX (green). (B) DCX-positive neurons (green) and astrocytes (GFAP, red) can be co-cultured for at least 1 - 2 weeks prior to analysis. For a detailed co-culture protocol, please see the Methods Library.
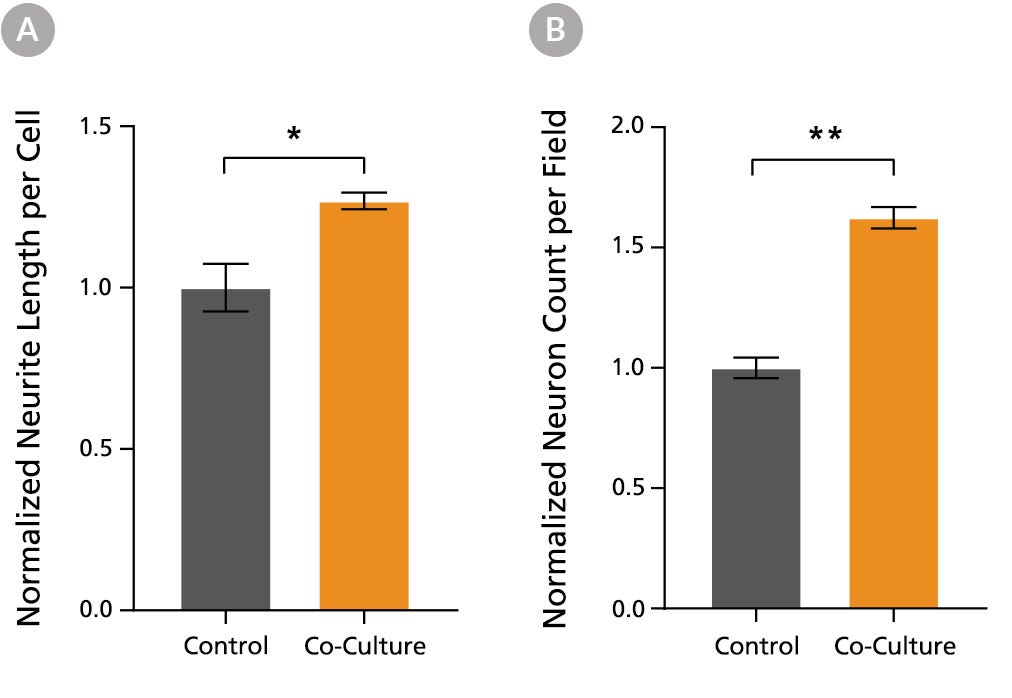
Figure 6. PSC-Derived Neurons Survive and Mature when Co-Cultured with PSC-Derived Astrocytes
NPCs generated from the STiPS-R038 cell line were differentiated to astrocytes using STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation and Maturation Kits. STiPS-M001 cell-derived NPCs were differentiated to forebrain-type neurons using STEMdiff™ Forebrain Neuron Differentiation and Maturation Kits. After co-culture for one week, neurons (A) had significantly increased neurite outgrowth as measured on MAP2-positive neurons with the NeuriteTracer plugin for ImageJ (M Pool et al. J Neurosci Methods, 2008) and (B) were more numerous than neurons cultured alone using the same feeding schedule. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
请在《产品说明书》中查找相关支持信息和使用说明,或浏览下方更多实验方案。
本产品专为以下研究领域设计,适用于工作流程中的高亮阶段。探索这些工作流程,了解更多我们为各研究领域提供的其他配套产品。
Thank you for your interest in IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human). Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
| 物种 | 人类 |
|---|

无血清神经添加物(50X)
提升神经元功能的无血清基础培养基
用于小鼠和人胚胎干细胞和iPS细胞的神经和胰腺分化

抗人、小鼠、大鼠β-球蛋白III的小鼠Monoclonal IgG2a抗体
扫描二维码或搜索微信号STEMCELLTech,即可关注我们的微信平台,第一时间接收丰富的技术资源和最新的活动信息。
如您有任何问题,欢迎发消息给STEMCELLTech微信公众平台,或与我们通过电话/邮件联系:400 885 9050 INFO.CN@STEMCELL.COM。
在线联系