技术资料
-
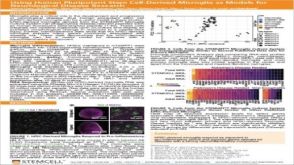 科学海报Using Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Microglia As Models For Neurological Disease Research
科学海报Using Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Microglia As Models For Neurological Disease ResearchConference:
FENS 2020


 EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒
EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒












 沪公网安备31010102008431号
沪公网安备31010102008431号