技术资料
-
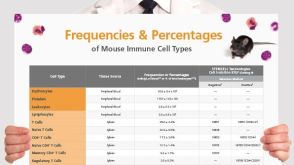 挂图Frequencies and Percentages of Mouse Immune Cell Types List of the frequencies of over 25 immune cell types in C57BL/6 mice
挂图Frequencies and Percentages of Mouse Immune Cell Types List of the frequencies of over 25 immune cell types in C57BL/6 mice -
 挂图Frequencies of Human Cell Types in Blood-Related Sources List of the frequencies of over 35 cell types in normal human blood-related sources.
挂图Frequencies of Human Cell Types in Blood-Related Sources List of the frequencies of over 35 cell types in normal human blood-related sources. -
 产品手册Human Primary Cells: It All Starts with the Right Cells
产品手册Human Primary Cells: It All Starts with the Right Cells品牌:
MegaCult,EasySep,MesenCult,MyeloCult,StemSpan


 EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒
EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒














 沪公网安备31010102008431号
沪公网安备31010102008431号