技术资料
-
 20:15
线上讲座STEMCELL Seminar: At the Origin of Intestinal Epithelial Stem Cells and Beyond发布日期: 11/20/2019
20:15
线上讲座STEMCELL Seminar: At the Origin of Intestinal Epithelial Stem Cells and Beyond发布日期: 11/20/2019 -
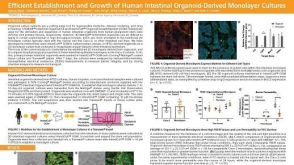 科学海报Efficient Establishment and Growth of Human Intestinal Organoid-Derived Monolayers
科学海报Efficient Establishment and Growth of Human Intestinal Organoid-Derived MonolayersConference:
ISSCR 2019


 EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒
EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒














 沪公网安备31010102008431号
沪公网安备31010102008431号