搜索结果: 'methocult media formulations for mouse hematopoietic cells serum containing'
-
 冻存的人外周血CD19+ B细胞 冻存的人原代细胞
冻存的人外周血CD19+ B细胞 冻存的人原代细胞 -
 冻存的人外周血CD4+ T细胞 冻存的人原代细胞
冻存的人外周血CD4+ T细胞 冻存的人原代细胞 -
 疾病状态人外周血制品,化脓性汗腺炎 新鲜或冻存的人原代细胞
疾病状态人外周血制品,化脓性汗腺炎 新鲜或冻存的人原代细胞 -
 患病的人外周血制品,炎性肌病 新鲜或冻存的人原代细胞
患病的人外周血制品,炎性肌病 新鲜或冻存的人原代细胞 -
 冻存的人外周血CD8+记忆T细胞 冻存的人原代细胞
冻存的人外周血CD8+记忆T细胞 冻存的人原代细胞 -
 小鼠IL-2酶联免疫吸附测定试剂盒 用于小鼠白细胞介素2的检测和测定
小鼠IL-2酶联免疫吸附测定试剂盒 用于小鼠白细胞介素2的检测和测定 -
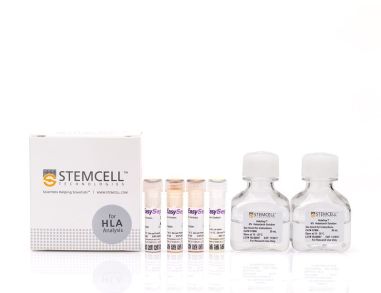 EasySep™ HLA总淋巴细胞富集: 用于处理全血的完整试剂盒
EasySep™ HLA总淋巴细胞富集: 用于处理全血的完整试剂盒通过免疫磁珠负选直接从HetaSep™处理的全血或洗涤后的白细胞单采术样本中分离出无标记的人淋巴细胞。
-
 重组小鼠干扰素γ 干扰素-γ
重组小鼠干扰素γ 干扰素-γ -
 重组小鼠 IL-17A 白介素17A
重组小鼠 IL-17A 白介素17A -
 重组小鼠Shh Sonic hedgehog
重组小鼠Shh Sonic hedgehog -
 重组小鼠TNF - α 肿瘤坏死因子
重组小鼠TNF - α 肿瘤坏死因子 -
 重组小鼠TPO 血小板生成素
重组小鼠TPO 血小板生成素


 EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒
EasySep™小鼠TIL(CD45)正选试剂盒





 沪公网安备31010102008431号
沪公网安备31010102008431号